A computer motherboard, also known as a mainboard, baseboard, or system board, is the primary circuit board of a computer. It is the backbone of a computer, connecting and communicating between all the other hardware components.
Here are some of its primary components and features:
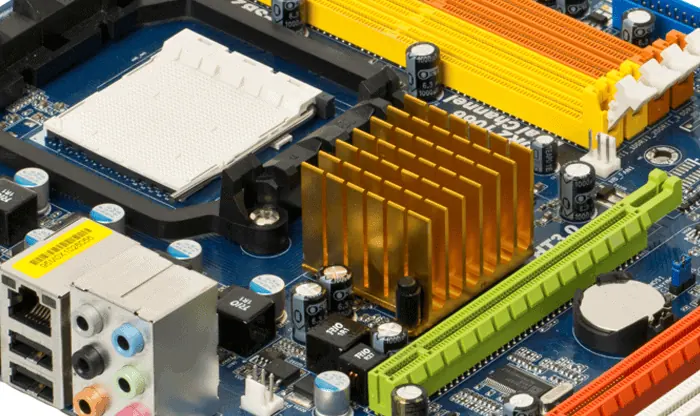
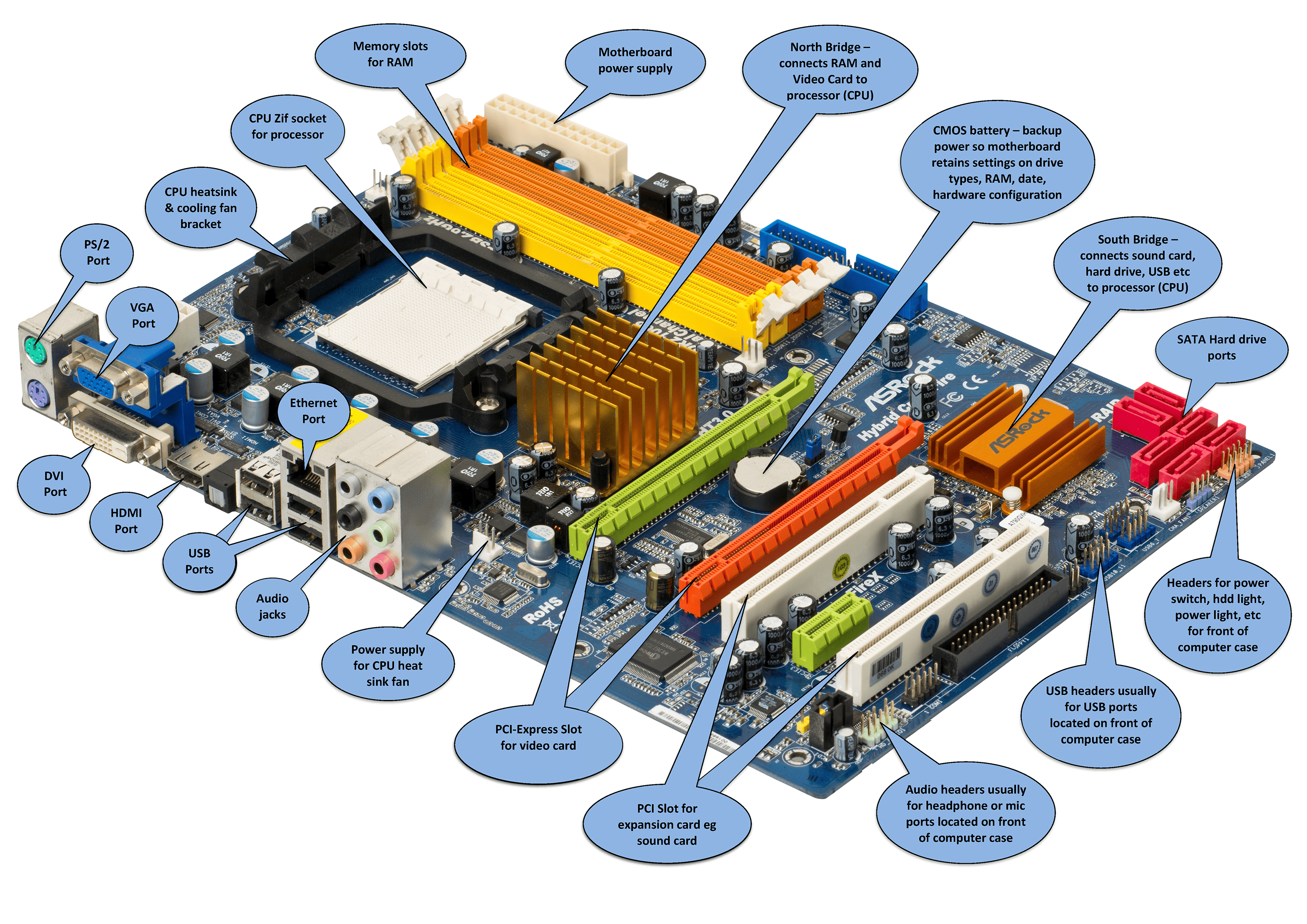
- Processor Socket: This is where the CPU (Central Processing Unit) is inserted. It’s designed to fit specific types of processors, from the likes of Intel and AMD. Not all CPUs work with all motherboards. The CPU and motherboard must both support the same CPU socket type (for example, Intel’s LGA 1151 or AMD’s AM4) to be compatible.
- Memory Slots: These slots hold RAM (Random Access Memory). The number of slots can vary, but typical consumer-level motherboards have between 2 and 8 slots. The type of slot (e.g., DDR3, DDR4, DDR5) will depend on the motherboard.
- Expansion Slots: These slots (commonly PCI, PCI Express) are used for additional hardware such as graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, additional USB slots, etc.
- BIOS/UEFI Chip: This is a chip that contains the basic instructions that guide the computer during startup.
- SATA Ports: SATA ports connect to storage devices like hard drives and SSDs. They transmit data between the motherboard and the storage devices.
- USB Headers: These are used to connect additional USB ports that are often found on the front of a computer case.
- Power Connectors: These are where you connect the power supply to the motherboard.
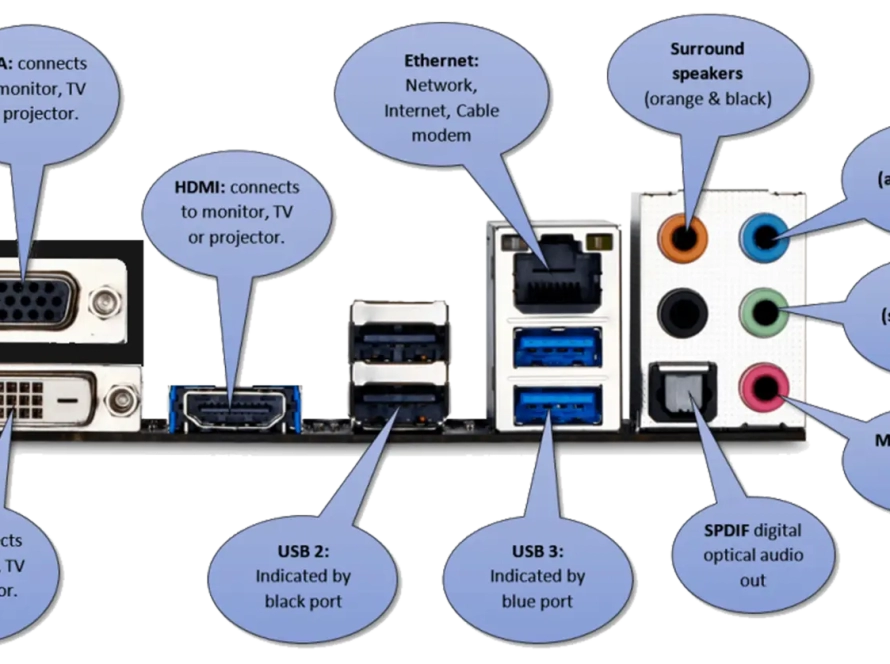
- Rear Panel Connectors: These include various connections like USB ports, audio input/output, Ethernet, display outputs, and more.
- Chipset: The chipset controls how data flows between the CPU and other components. It is usually made up of two chips: the northbridge, which controls the fastest interfaces (like the connection to graphics cards and RAM), and the southbridge, which controls slower peripherals (like the SATA or USB connections).
- CMOS battery: A small, round, silver coin-cell battery (often a CR2032), provides power to the CMOS RAM so it can retain certain system information when the computer is powered off or unplugged. This includes settings like system time and date, as well as hardware settings stored in the BIOS or UEFI, like boot order, overclocking parameters, and other system-specific details.
- Ports and Connectors: Motherboards offer a variety of ports and connectors for peripherals and other devices. These include USB ports, HDMI ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, and more. Some motherboards may also have ports for more specialized hardware, like high-end audio equipment or professional-grade video editing hardware.
- Expansion Capabilities: Most motherboards provide a number of slots such as PCI express for installing additional components like sound cards, graphics cards, and other types of expansion cards. The number and type of these slots can vary depending on the motherboard.
- Onboard Features: Some motherboards come with integrated features such as a graphics processor, sound card, or Wi-Fi adapter. These can be useful for saving space or money, but they may not offer the same performance as standalone components.
- BIOS/UEFI: The BIOS/UEFI is a program that the computer’s processor runs when the computer is turned on. It manages data flow between the computer’s operating system and the attached devices like hard disk, video adapter, keyboard, mouse, and printer.
- Form Factor: This refers to the physical layout and size of the motherboard. It determines what type of case and power supply you’ll need, how many ports you’ll have, and how many components you’ll be able to install. The most common form factors are ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX.
A motherboard is a complex piece of technology that serves as the hub for all of the computer’s components. It is responsible for coordinating and allowing communication between the components, making it one of the most important parts of any computer. Understanding the intricacies of your motherboard can help you better understand how your computer works and make more informed decisions when it comes to upgrading or building your own PC.